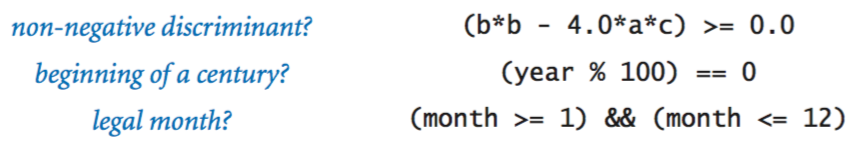class Coffee extends Beverage {
public Coffee() {
}
public void addSugar(int cubes) {
System.out.println("You added " + cubes + " sugar cubes.");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Coffee myOrder = new Coffee();
myOrder.addSugar(2);
myOrder.isFull();
}
}
The
void keyword indicates that no value should be returned by the method after it executes all the logic in the method. If we do want the method to return a value after it finishes running, we can specify the return type.- The
voidkeyword (which means "completely empty") indicates to the method that no value is returned after calling that method. - Alternatively, we can use data type keywords (such as
int,char, etc.) to specify that a method should return a value of that type.
Java is a programming language designed to build secure, powerful applications that run across multiple operating systems, including Linux, Mac OS X, and Windows. The Java language is known to be flexible, scalable, and maintainable.
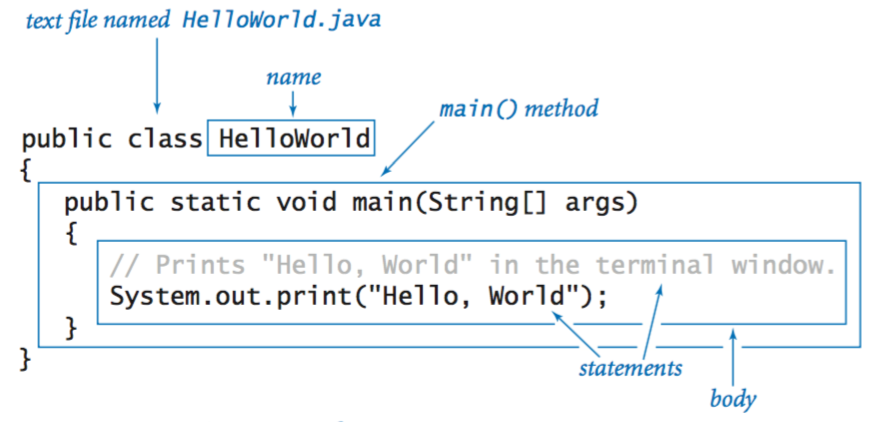
Hello, World.
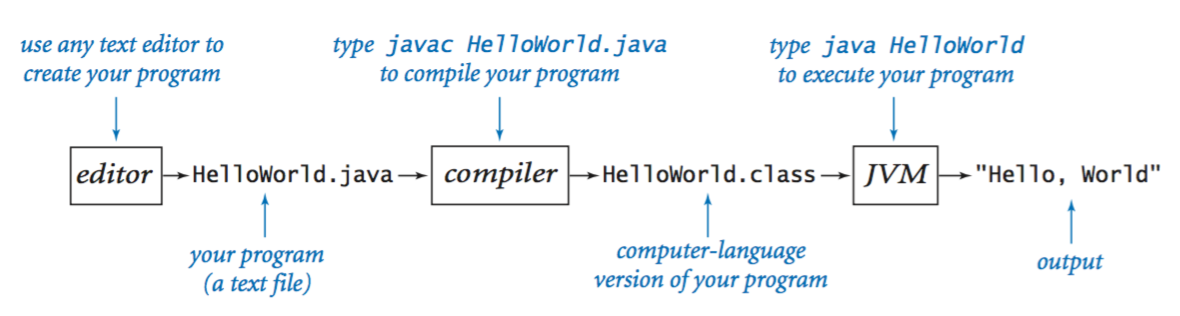
Editing, compiling, and executing.
Built-in data types.
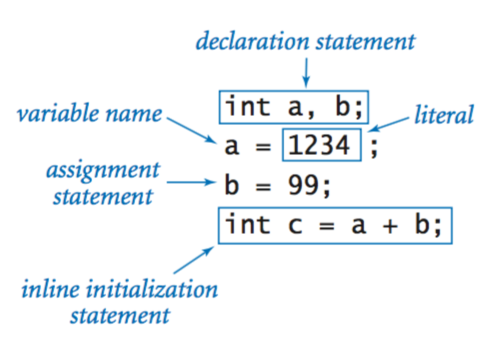
Declaration and assignment statements.
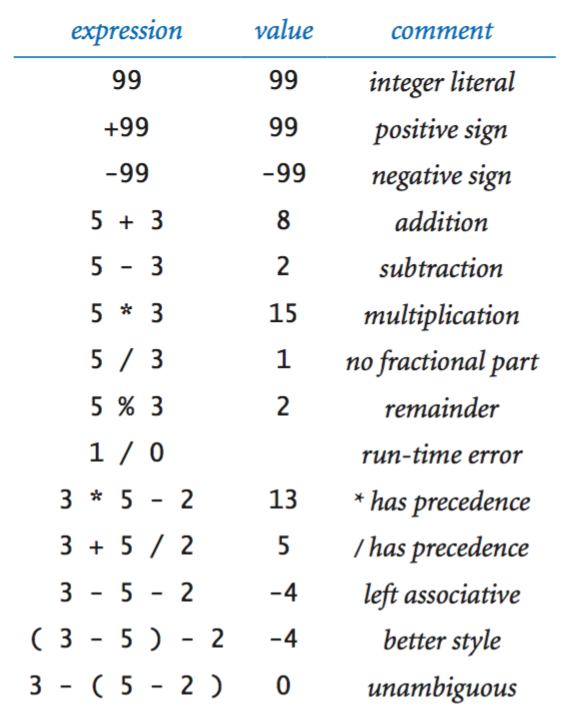
Integers.
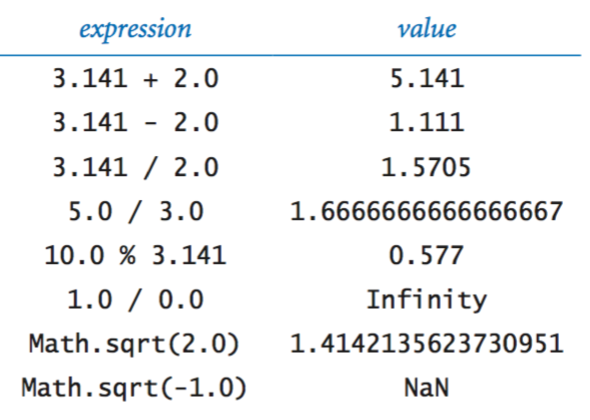
Floating-point numbers.
Booleans.
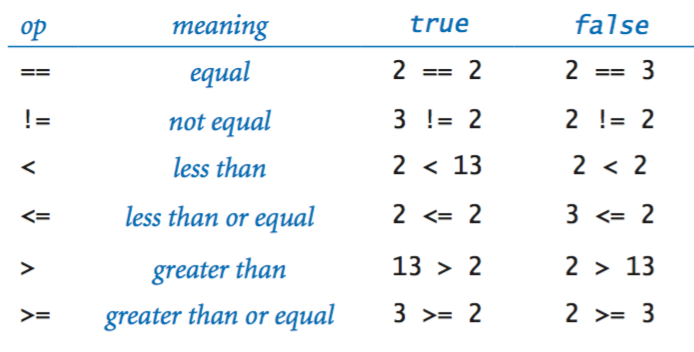
Comparison operators.
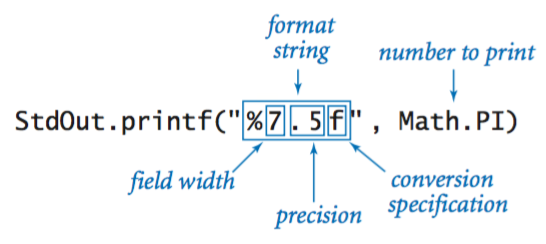
Printing.
Parsing command-line arguments.
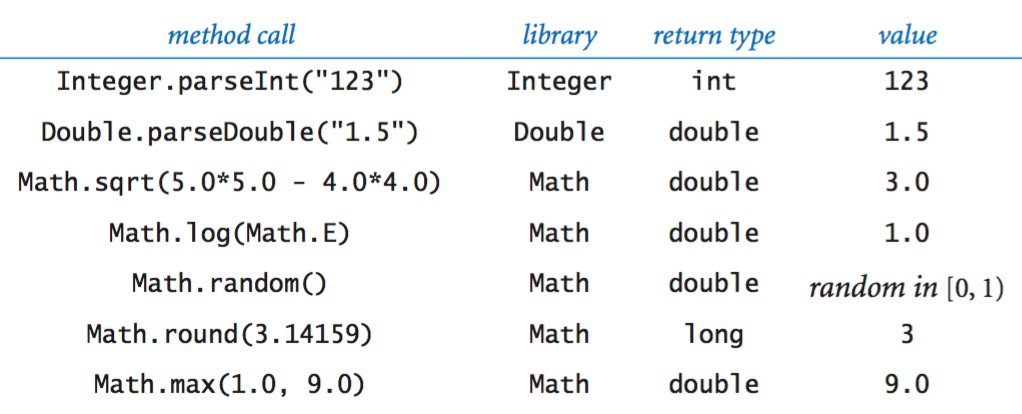
Math library.
The full java.lang.Math API.
Java library calls.
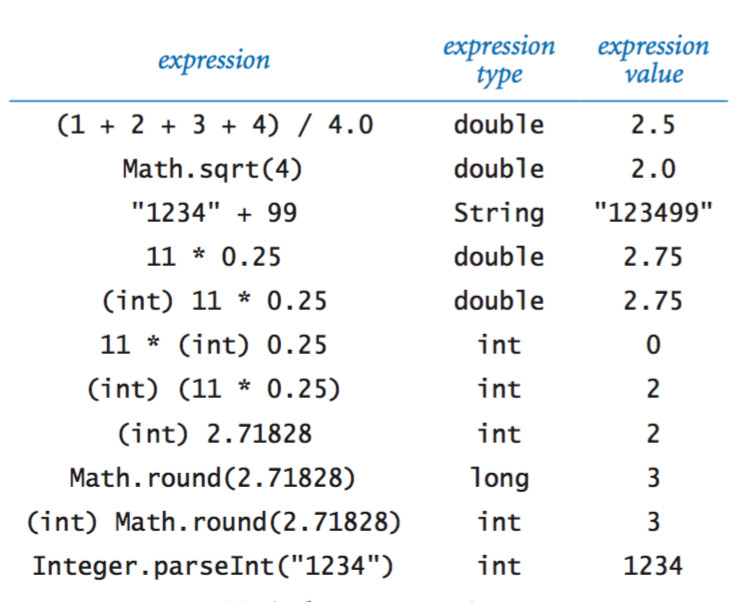
Type conversion.
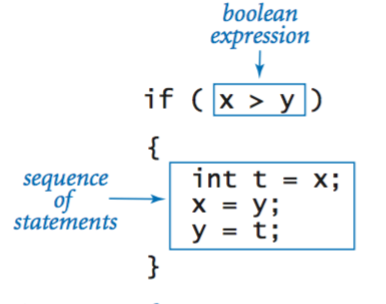
Anatomy of an if statement.
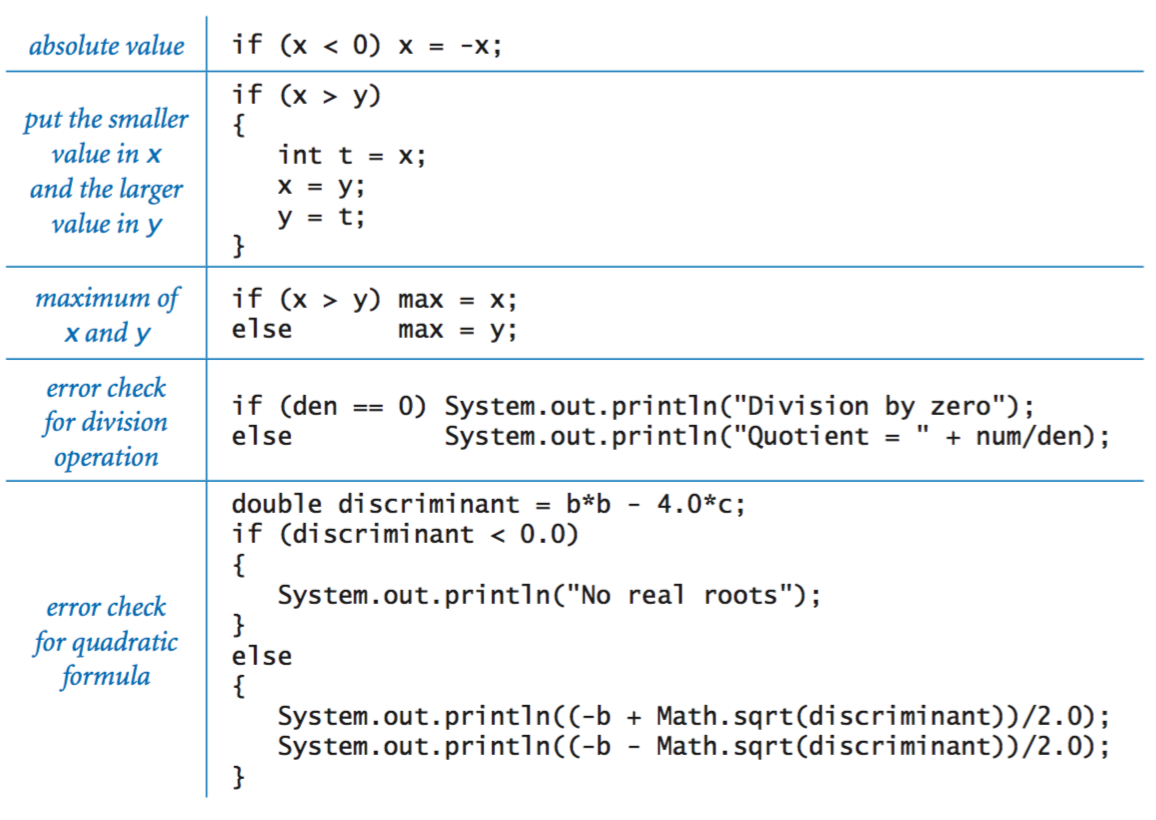
If and if-else statements.
Nested if-else statement.
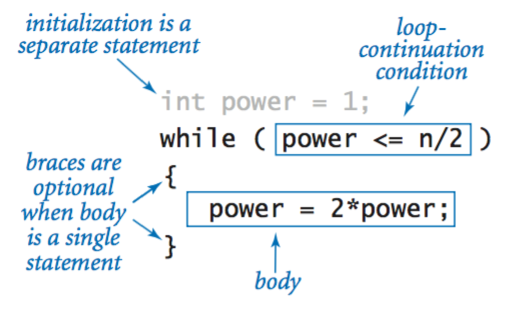
Anatomy of a while loop.
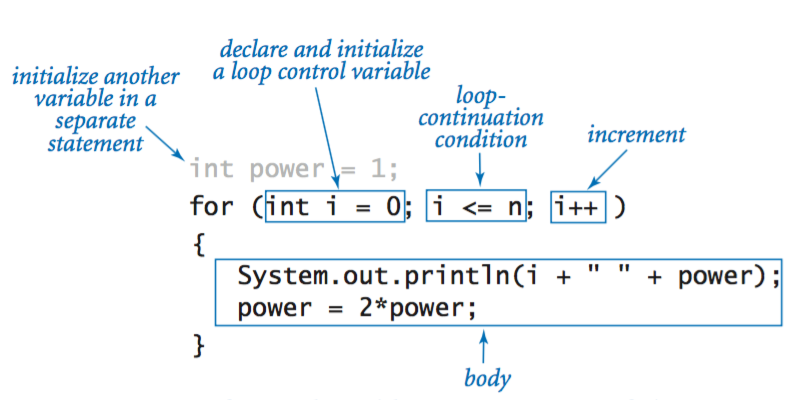
Anatomy of a for loop.
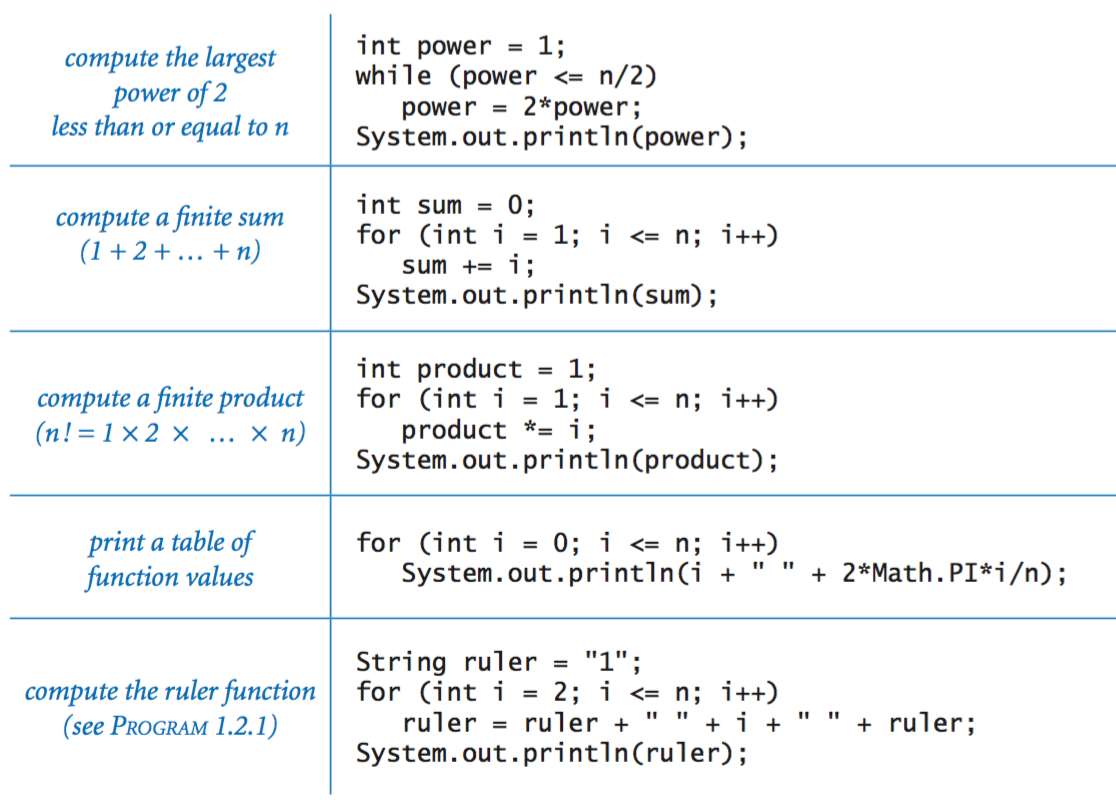
Loops.
Break statement.
Do-while loop.
Switch statement.
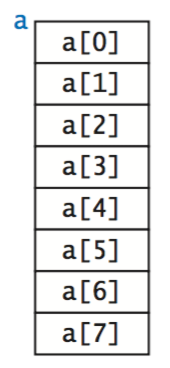
Arrays.
Inline array initialization.
Typical array-processing code.
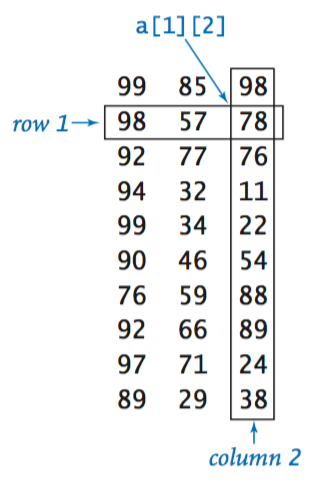
Two-dimensional arrays.
Inline initialization.
Our standard output library.
The full StdOut API.
Our standard input library.
The full StdIn API.
Our standard drawing library.
The full StdDraw API.
Our standard audio library.
The full StdAudio API.
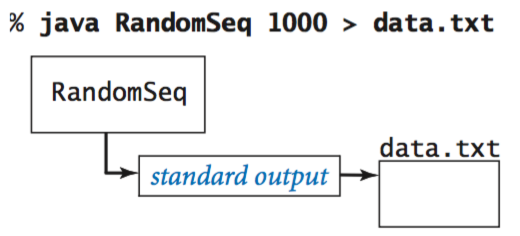
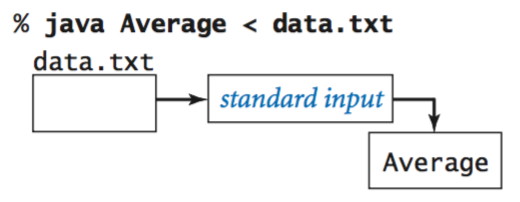
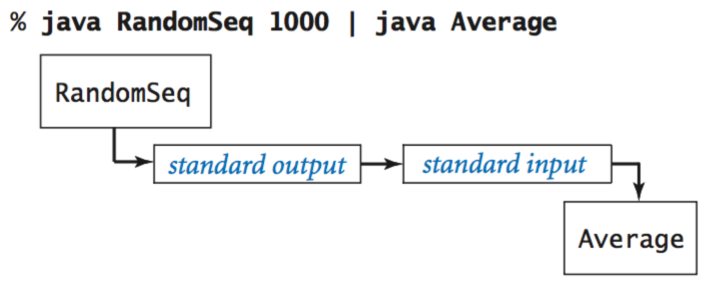
Redirection and piping.
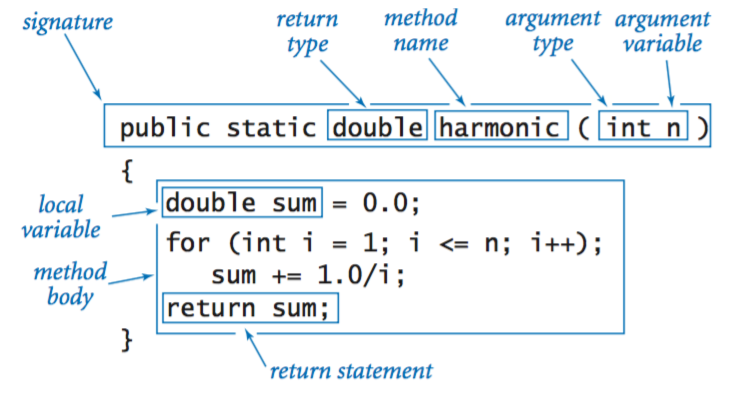
Functions.
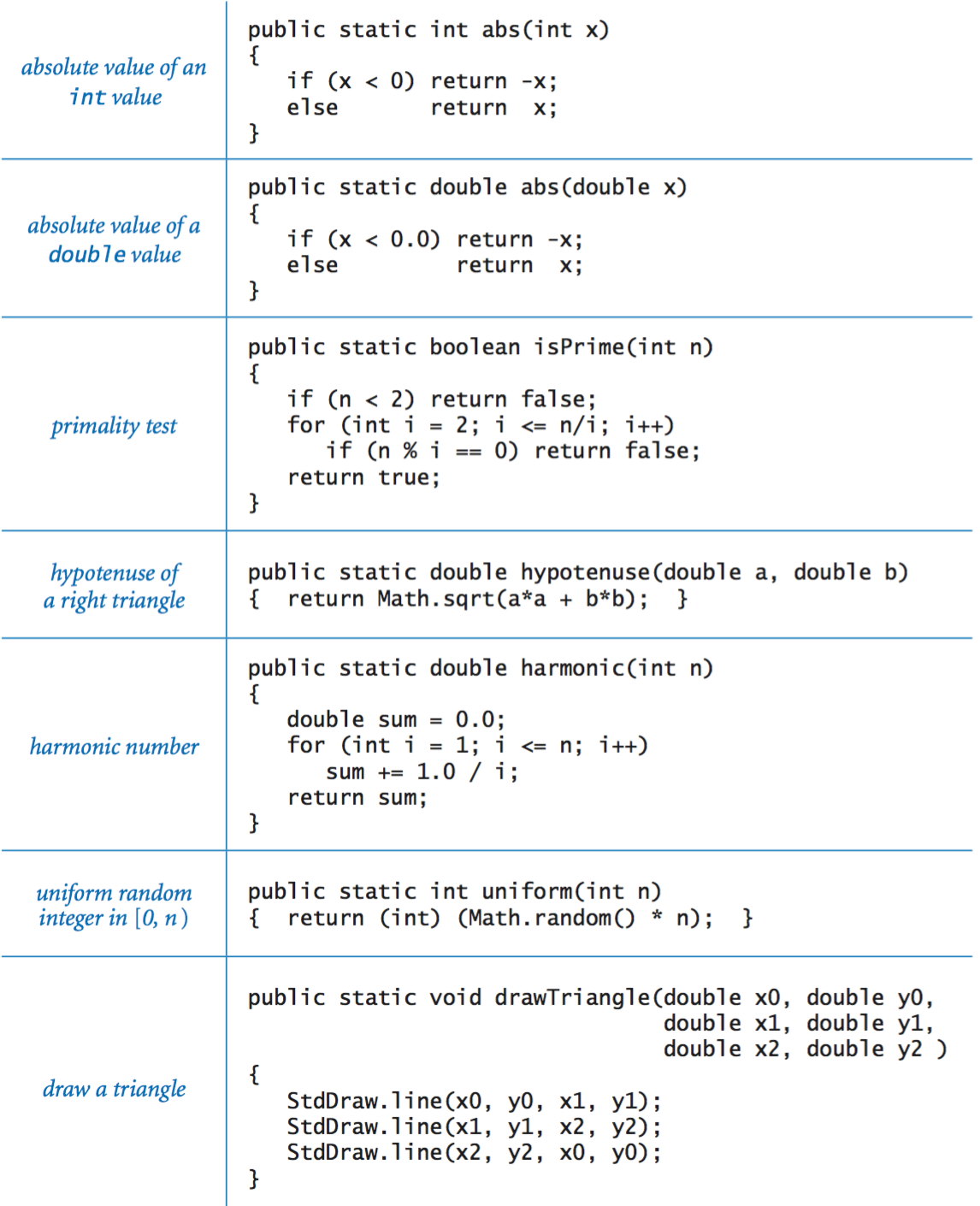
Libraries of functions.
Our standard random library.
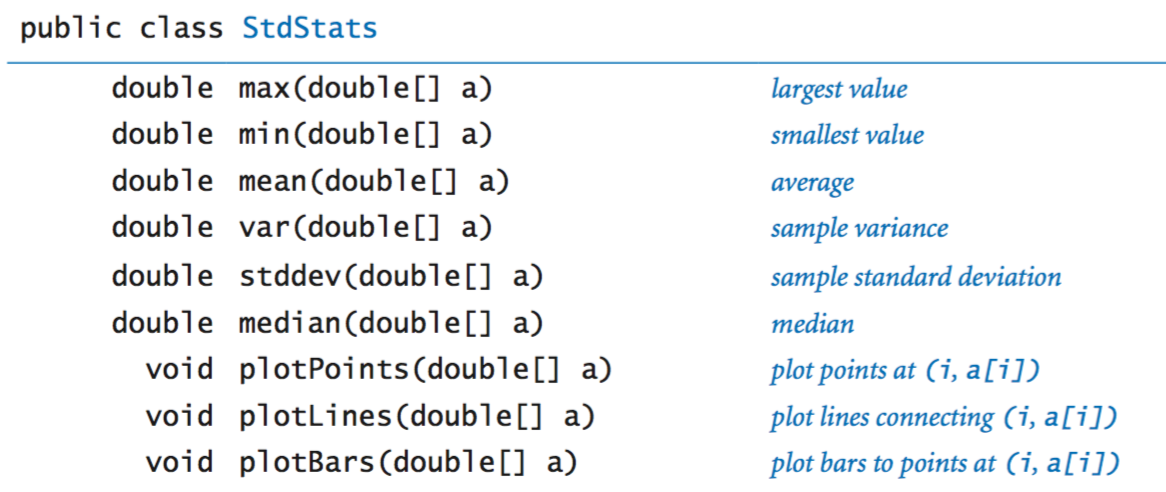
Our standard statistics library.
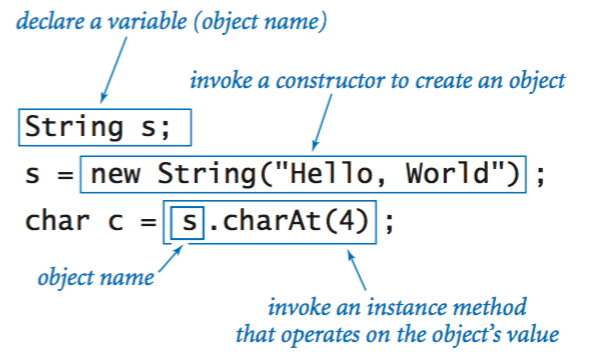
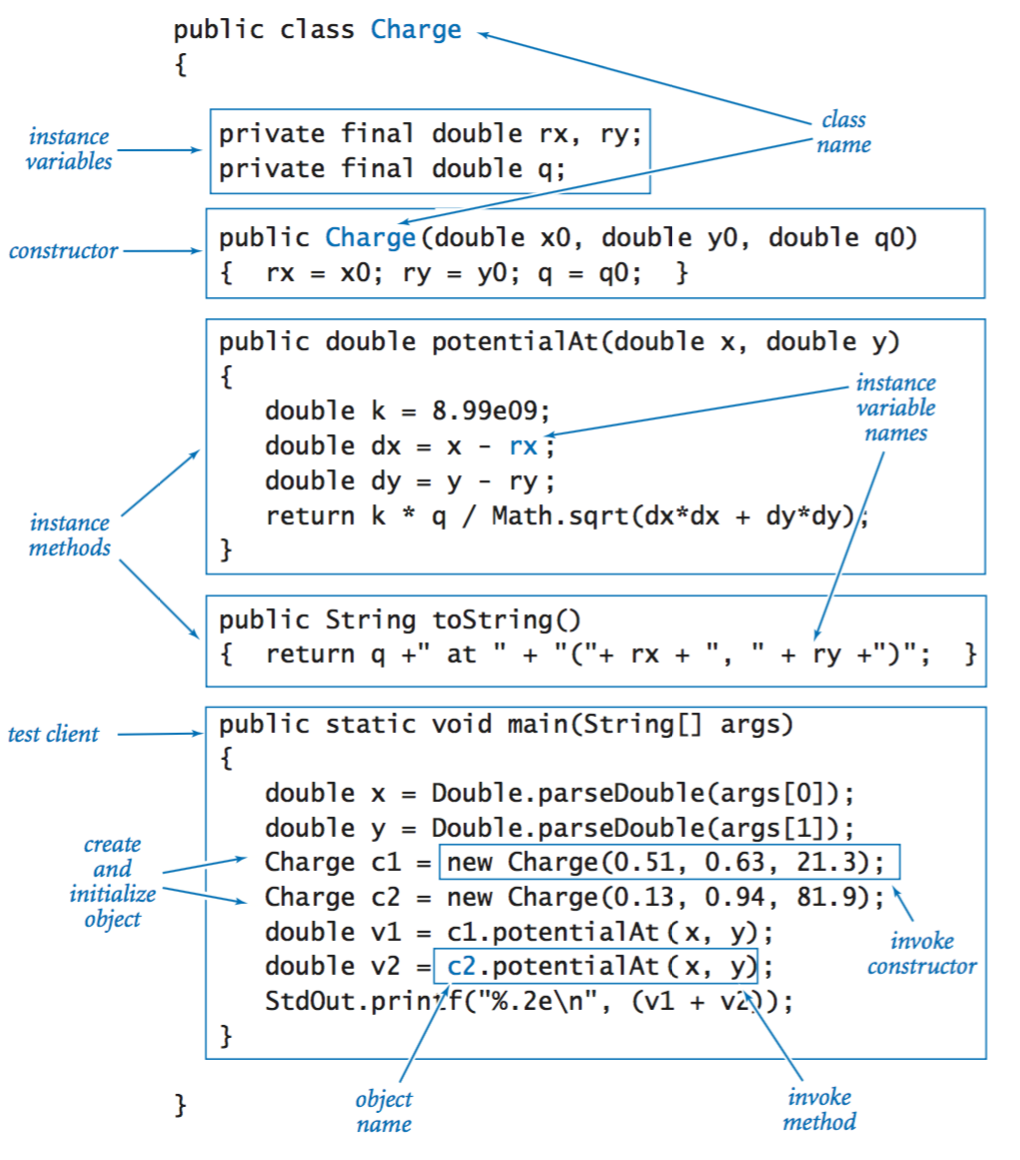
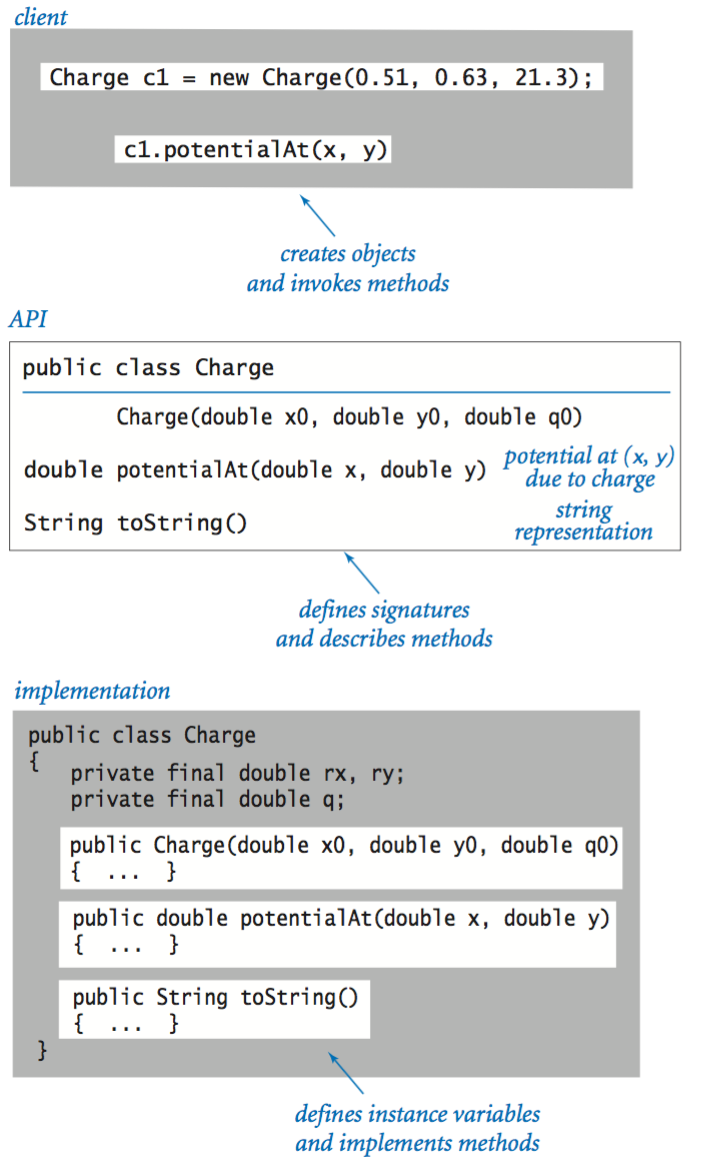
Using an object.
Instance variables.
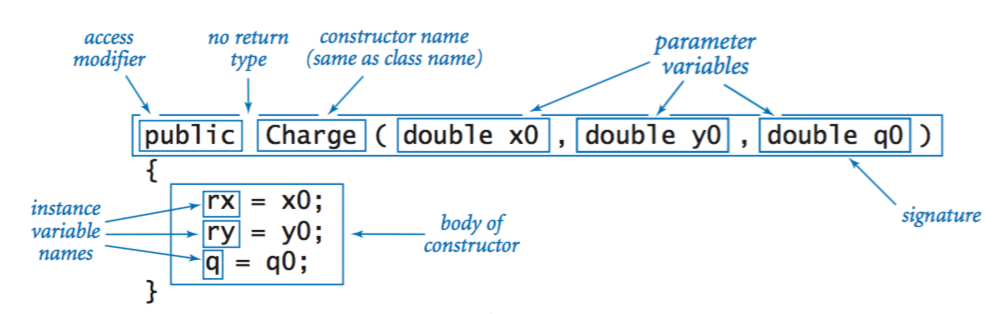
Constructors.
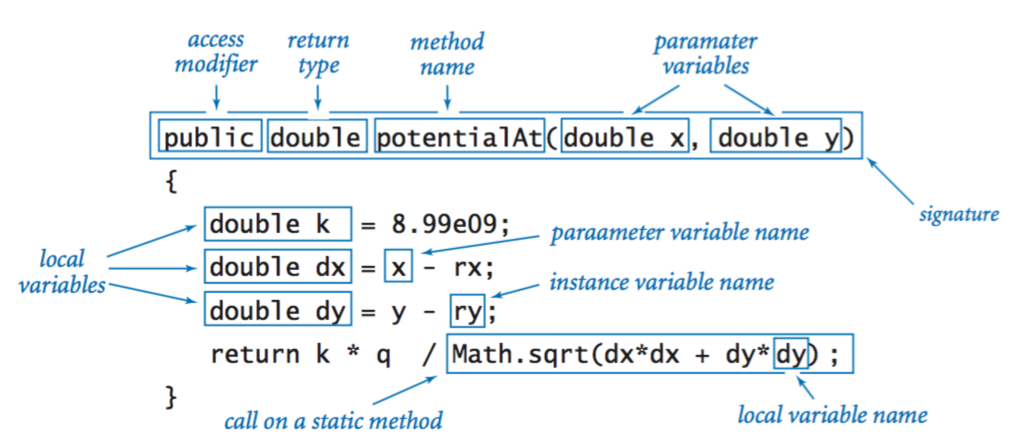
Instance methods.
Classes.
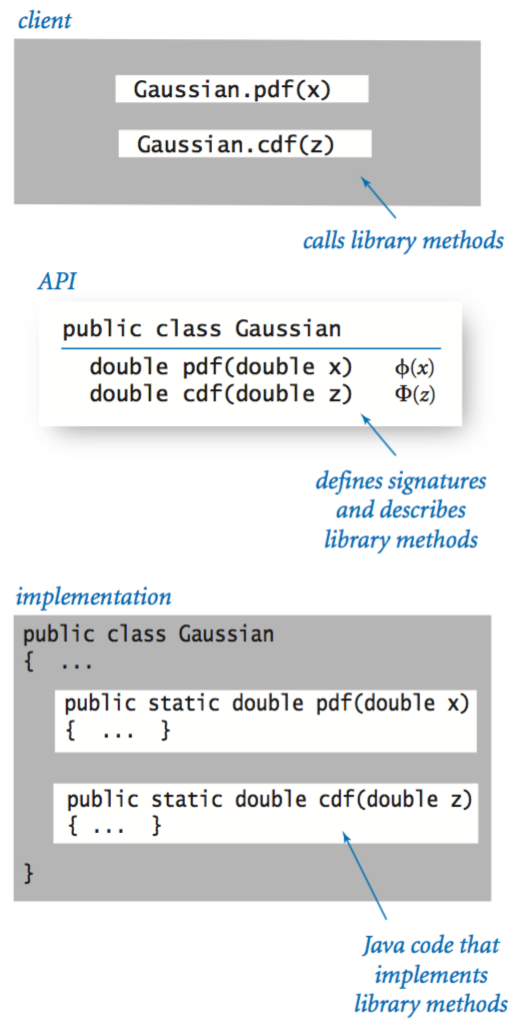
Object-oriented libraries.
Java's String data type.
The full java.lang.String API.
Java's Color data type.
The full java.awt.Color API.
Our input library.
The full In API.
Our output library.
The full Out API.
Our picture library.
The full Picture API.
Our stack data type.
The full Stack API.
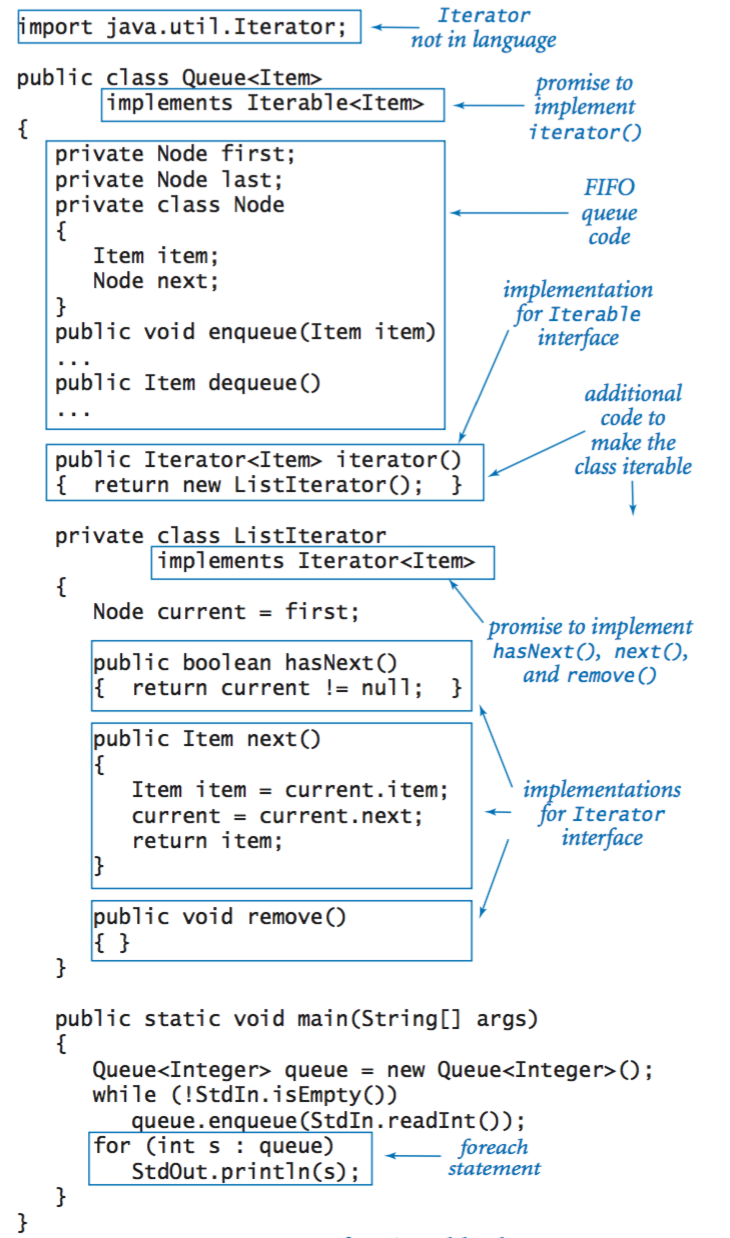
Our queue data type.
The full Queue API.
Iterable.
Our symbol table data type.
The full ST API.
Our set data type.
The full SET API.
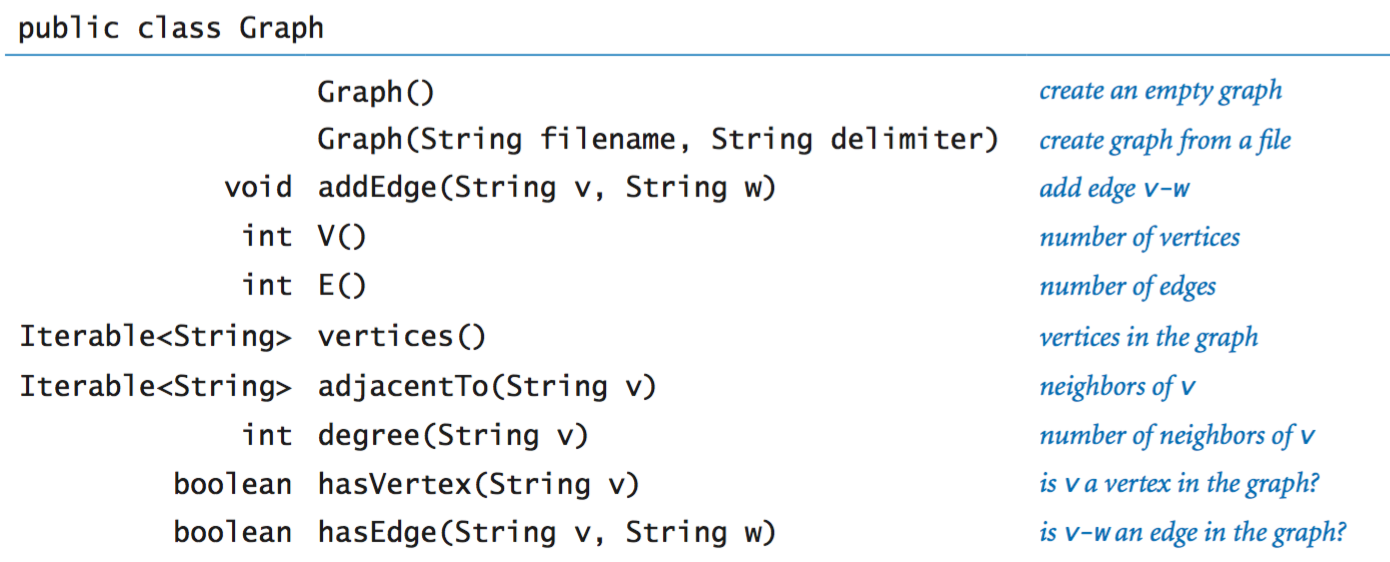
Our graph data type.